- Success Stories, Uncategorized
- Satellite Science & Environmental Intelligence
Engaging in New and Emergent Satellite Technologies
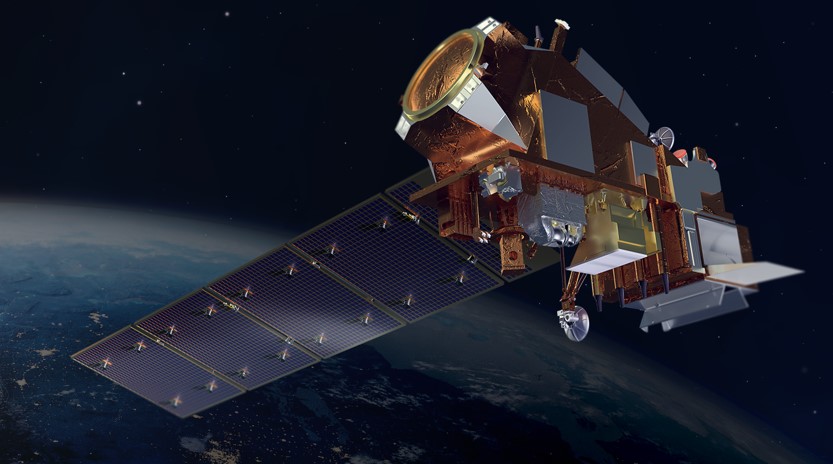

CSS employee owners (formerly Riverside employees) support the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service’s (NESDIS) Center for Satellite Applications and Research (STAR). STAR is the science arm of NESDIS, which acquires and manages the nation’s environmental satellites for NOAA. Satellite observations are critical to informing situational awareness and numerical weather prediction applications. These applications provide guidance to users and stakeholders on environmental threats at multiple timescales, from current analyses to medium-range and seasonal-to-subseasonal lead times.
As a subtask, CSS employee owners support the NESDIS Research and Technology Maturation for Exploitation of Emerging Technology (RTMEE). Objectives for this task are to ensure STAR is engaged in new emerging technologies, numerical techniques, new observing systems and in supporting next-generation systems, to keep all aspects of STAR activities relevant for the future. This is achieved by undertaking research and technology maturation activities that will transition to supporting mission activities and advanced programs in NOAA. The work will ensure that the quality of the data produced by NOAA meet or exceed international standards.

For their role, CSS employee owners supporting RTMEE are responsible for collaborating with NESDIS Systems Architecture and Engineering (SAE) and STAR staff to explore new technologies in support of NOAA’s mission. CSS leverages SAE and STAR expertise in satellite data and applications required to address the needs of data exploitation, validation, verification, and quality and impact assessment opportunities. CSS supports the advancement of NOAA’s observational and data system capabilities with both internal and external NOAA partners and demonstrates the value of artificial intelligence to efficiently exploit the information content of microwave sensor concepts and quantify the impact on NOAA systems. In addition, we support the evaluation and exploitation of 3D-wind measurements to help determine the impact of the potential deployment of new types of satellite sensors dedicated to filling gaps to improve the quality of weather and climate data.
Feature photo credit: Artist rendering of NOAA 21 satellite (credit: NOAA)
See More CSS Insights

Over 40 Years of Support
Since 1982, members of our staff have supported EPA’s Office of Pesticide Programs. As part of this contract, our staff assess environmental and human health impacts on anthropogenic chemicals. The agricultural industry is critical to food and textile production, it is a large contributor to the U.S. economy. Not only does the industry provide food…
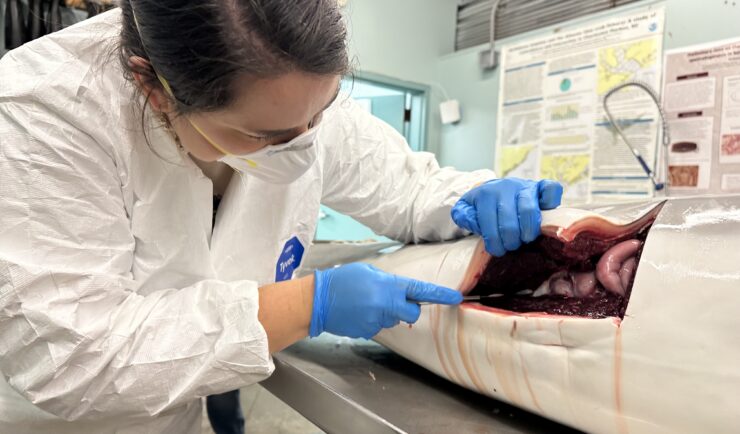
Assisting South Carolina Marine Mammal Stranding Network
CSS employee owner and Marine Mammal Microplastic Specialist supporting NOAA’s National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science assists the South Carolina Marine Mammal Stranding Network in responding to dead marine mammals when they strand on beaches or estuaries throughout South Carolina. This is work is critical for human and environmental health because it provides invaluable samples…
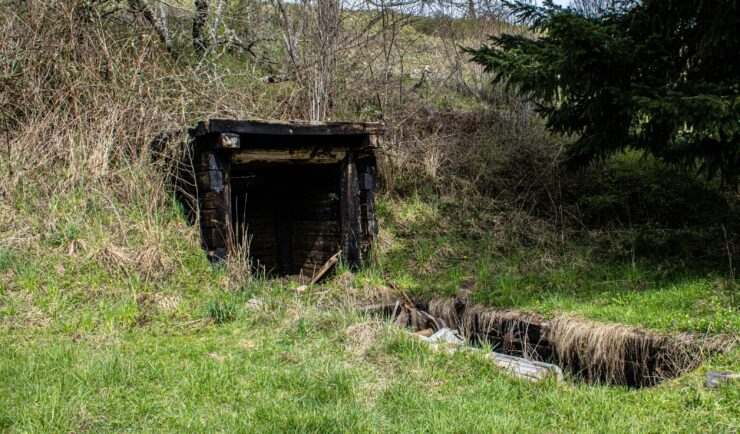

Assessing Contamination in Abandoned Mines
CSS supports the Environmental Protection Agency with assessing contamination within abandoned mines. There are thousands of abandoned mines throughout the western United States. Many of these mines are leaching heavy metals into nearby streams or have contaminated soils causing vegetation die off. CSS employee owners conduct field work to assess the extent of this contamination.…
